
2025-03-12
As the sophistication and frequency of information security attacks continue to increase, the number of organizations being targeted from those attacks is also increasing, regardless of the organizations’ size, industry, location, or reputation. Hence, the need for following an effective approach for information security governance has become inevitable.
Organizations that rely only on incident response plans for addressing information security incidents are usually not successful in reducing these incidents and their impact. Instead, they should implement information security management systems (ISMSs) that integrate various policies, processes, procedures, and activities for ensuring and maintaining information security.
ISMSs enable the creation of standardized procedures to select and implement adequate information security controls and manage them effectively. An ISMS that is suitable to the organization’s mission and objectives helps in reducing the likelihood and impact of information security risks.
While ISO/IEC 27001 provides the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an ISMS, ISO/IEC 27002 provides the controls for managing risks within that ISMS. These controls are based on internationally recognized best practices and can be implemented by organizations of all types and sizes.
The importance of information security has increased significantly over the years as the number of organizations that collect, process, store, and transmit information daily and in many forms has also grown.
What is information security? This term refers to the actions that organizations take to prevent unauthorized access to, use, alteration, and destruction of information. This term is often used together with cybersecurity; however, they are not synonymous. While information security ensures the protection of different types of information, within and beyond the cyberspace, cybersecurity refers to the protection of organization’s data, devices, systems, and networks in cyberspace.
Information security is defined as the preservation of the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (commonly known as the CIA triad) of information. Regardless of the type of information, information security aims to ensure authorized access to data (confidentiality), authorized alteration of data (integrity), and timely accessibility (availability) to data.
ISO/IEC 27001 provides a robust framework through its requirements outlined in clauses 4 to 10 and a comprehensive list of information security controls that enable effective information security management. The standard promotes a risk-based approach which requires organizations to identify, analyze, and evaluate information security risks and implement adequate controls to treat them. After the initial implementation is completed, the standard requires organizations to monitor and review the ISMS regularly, to ensure its ongoing effectiveness in protecting information assets.
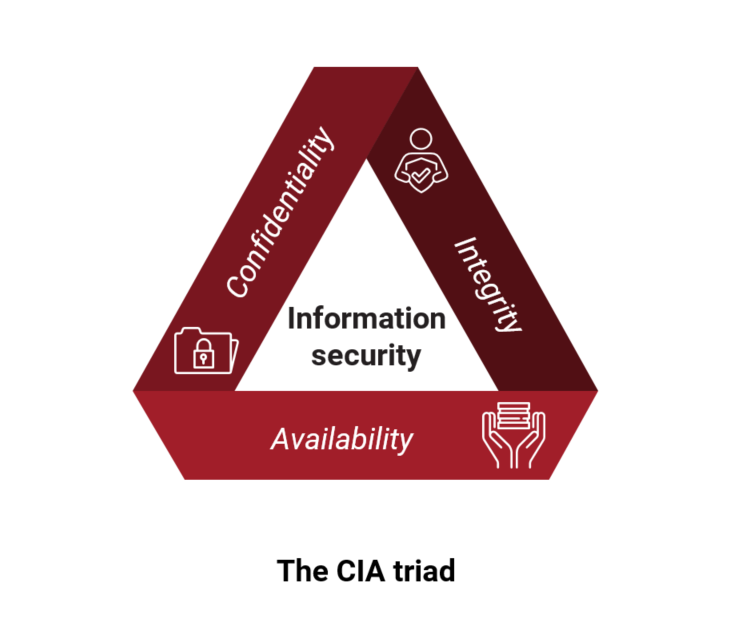
Confidentiality refers to the protection of information from unauthorized access. Organizations ensuring the confidentiality of information keep important information private and ensure that the information is used only by authorized parties. Typical threats to the confidentiality of information are phishing, malware, password attacks, insider threats, man-in-the middle attacks, data mining, and eavesdropping attacks.
There are various controls that organizations can implement to ensure the confidentiality of their data, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, the principle of least privilege, secure disposal of data, and physical access controls. Security controls for ensuring confidentiality should be selected based on the information classification and the potential business impact of its unauthorized disclosure.
Security controls that help in mitigating these threats include, among others, appropriate access management, user trainings, hashing techniques, and digital signatures. Moreover, backup procedures are crucial for ensuring integrity since they enable organizations to restore information that has been altered.
Availability ensures that information is accessed by authorized individuals as required, when and where required, and by the person(s) requiring it. Some of the main challenges to the availability of information include Denial-of-Service attacks (DoS), technical failures, natural disasters, human errors, and insufficient communication bandwidth. In practice, availability of information can be ensured through appropriate resilient system architecture, backup procedures, capacity planning, incident management, maintenance of equipment, and business continuity planning.
For example, a bank, whose mobile banking application processes and collects personal data, should ensure that the data is protected from unauthorized access and modification and that it can be accessed by the users, e.g., when making transactions online. The CIA triad of financial transactions completed online can be improved as follows:
Cybersecurity refers to the protection of digital information in computers, systems, and networks from cyberattacks. The number of cyberattacks has increased considerably in the recent years. According to CyberEdge’s published report in 2022, 85.3% of organizations that were part of the study claimed that their networks had been compromised from cyberattacks at least once during 2021. In addition, 27.9% of these organizations had experienced between 6 and 10 cyberattacks within the same period. These high percentages emphasize the importance of implementing effective cybersecurity solutions that enable organizations to continually monitor and prevent cyber attacks and reduce their impact..
Cybersecurity covers various categories including network security, application security, information security, operational security, disaster recovery and business continuity, and end-user education. Individuals with malicious intents may access the network of organizations by exploiting misconfigured firewalls, unsecured wireless routers, and infected laptops and ports.
Assets in the cloud and employees’ devices when implementing a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policy or when working remotely are also potential targets of cyberattacks due to the lack of control from organizations. Some of the cyberthreats that organizations should be prepared for in 2022 include social engineering, ransomware, advanced persistent threats, disgruntled employees, supply chain attacks, operational technology (OT) security threats, and IoT-related threats.
In 2016, the European Union introduced the NIS (Network and Information Systems) Directive, a cybersecurity legislation, with the aim of increasing cybersecurity across EU countries. The directive was then enacted into EU member states’ laws. The NIS Directive will ensure that EU member states are prepared for cyberattacks and have established incident response teams. In addition, by establishing cooperation groups, it will enable the states to cooperate with one another and establish mechanisms through which information is exchanged more easily between them. Lastly, it will promote a culture of cybersecurity across the countries.
Privacy is considered a fundamental human right. As defined by EDPS (European Data Protection Supervisor), having privacy means “to be autonomous, in control of information about yourself, to be let alone.” The right to privacy is included, among others, in the UN Declaration of Human Rights, the European Convention of Human Rights, and the European Charter of Fundamental Rights. More than 150 nations have included the right to privacy in their national constitutions.
Data privacy protection relies on the effectiveness of information security controls. Some of today’s threats to privacy include online tracking, IoT attacks, and cyberattacks. Organizations that collect and process data should employ access control mechanisms, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, to ensure the protection of one’s information privacy.